Essential Phlebotomy Tools: A Complete Guide to Equipment & Best Practices
Performing safe and efficient blood collection, or phlebotomy, requires the right tools, proper techniques, and a good understanding of best practices. Whether you’re a seasoned healthcare professional,a trainee,or simply curious about what goes into blood draws,this comprehensive guide will walk you thru the essential phlebotomy tools,their roles,and how to use them properly. Let’s dive into the world of phlebotomy equipment and discover how to optimize your practice for safety, comfort, and accuracy.
Introduction to Phlebotomy and Its Importance
Phlebotomy,the process of drawing blood from patients,is a vital component of medical diagnostics,research,and donor collections. proper technique ensures reliable test results, minimizes patient discomfort, and reduces the risk of complications or infections. Selecting the appropriate tools and following best practices are crucial for achieving these goals.
Essential Phlebotomy Equipment and Their Functions
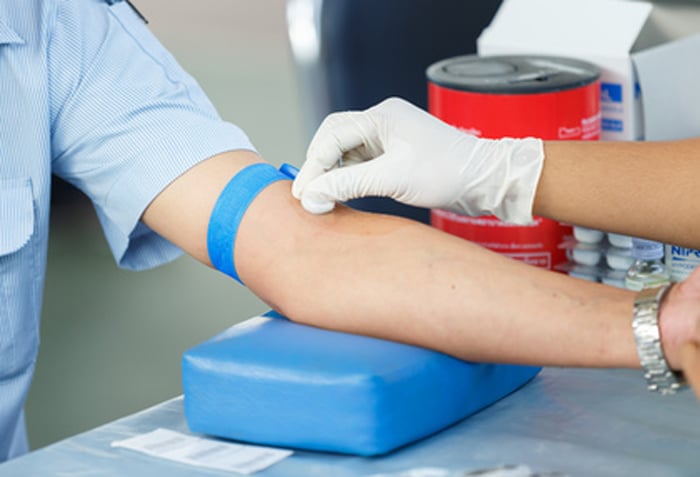
1. Tourniquets
- Purpose: To temporarily restrict blood flow and make veins more prominent for easier access.
- Types: Latex, latex-free, reusable or disposable.
- Best Practice: Always ensure tourniquets are snug but not overly tight to prevent discomfort or hematoma.
2. Needles & Syringes
- Types of Needles: Butterfly (winged infusion sets), straight needles, safety-engineered needles.
- gauge & Length: Commonly 21-23G,with lengths ranging from 1 to 1.5 inches, depending on venipuncture site and patient factors.
- Best Practice: Use the smallest gauge compatible with the procedure to reduce pain.
3. Vacuum Tubes & Blood Collection Sets
- Vacuum Tubes: Pre-sterilized tubes with specific additives (e.g., EDTA, serum separator).
- Blood Collection Sets: Comprise needle,holder,and tube adapters for efficient,one-handed blood collection.
- Best Practice: Choose the correct tube based on test requirements and fill tubes in the recommended order.
4. Lancets & Capillary Tools
- Request: For capillary blood collection, especially in infants or on fingerstick samples.
- Types: Standard lancets, safety lancets, micro-collection devices.
- Best Practice: use sterile, sharp lancets and follow safety protocols to prevent needlestick injuries.
5. Alcohol Swabs & skin Readiness Supplies
- purpose: To disinfect the puncture site before needle insertion.
- Best Practices: Use alcohol swabs and allow the skin to dry to reduce contamination and discomfort.
6. Bandages & adhesive Tapes
- Purpose: To secure the puncture site post-collection and prevent bleeding or hematoma.
- Types: Adhesive bandages, gauze pads, tape strips.
7. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Include: Gloves, face masks, protective eyewear.
- purpose: To protect both the patient and collector from infections and bloodborne pathogens.
Best Practices for Using Phlebotomy Equipment
Preparation & Patient Comfort
- Always verify the patient’s identity and test requisition.
- Explain the procedure clearly to the patient to reduce anxiety.
- Check all equipment for integrity and sterility before use.
Proper technique
- Apply the tourniquet correctly; it should be tight enough to occlude venous flow but not cause pain.
- Locate a suitable vein,typically the median cubital vein.
- Disinfect the site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
- Insert the needle at a 15-30 degree angle, bevel up, into the vein.
- Fill the vacuum tubes or draw blood into syringes carefully.
- Withdraw the needle smoothly, activate safety features if available, and apply pressure with gauze.
- Secure the puncture site with a bandage and assess for bleeding or hematoma formation.
Safety & Infection Control
- Dispose of sharps immediately in approved sharps containers.
- Use gloves and PPE at all times.
- Follow OSHA guidelines for bloodborne pathogen precautions.
Benefits of Using Proper Phlebotomy Equipment & Techniques
- Enhanced patient comfort and cooperation.
- Accurate and reliable test results.
- Minimized risk of hematomas,infections,and needlestick injuries.
- Improved efficiency and workflow for healthcare professionals.
Practical Tips & Common Pitfalls
- Always verify the correct tube order to avoid test contamination.
- Ensure the patient remains still during venipuncture.
- Do not reuse needles or tourniquets.
- Be attentive to signs of fainting or discomfort - stop and provide assistance if needed.
- Use the right equipment for challenging veins, such as butterfly sets or multi-sampling needles.
Case Study: Improving Blood collection Efficiency
| Scenario | action Taken | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Repeated difficult draws on elderly patient | Used smaller gauge butterfly needles and warmed the patient’s hand | Successful blood draw without patient discomfort |
First-Hand Experience & Personal Insights
As a healthcare professional with years of experience in phlebotomy, I’ve learned that the right equipment combined with thorough technique makes all the difference. Investing in high-quality, sterile supplies, paying attention to patient cues, and maintaining a calm, professional demeanor helps foster trust and improves outcomes.
Conclusion
In the world of clinical laboratory medicine, the importance of essential phlebotomy tools cannot be overstated. Proper equipment selection,adherence to best practices,and a patient-first approach ensure safety,accuracy,and comfort. Whether you’re preparing for your first blood draw or seeking to refine your skills, understanding these fundamental tools and techniques is key to becoming a proficient phlebotomist. Remember, excellence in blood collection starts with the right tools and a commitment to safety and professionalism!