How to Become a Certified Phlebotomy Technician: Your Guide to Top Phlebotomy Technician Schools
Introduction
If you’re curious about a healthcare career that combines science,patient interaction,and precision,becoming a certified phlebotomy technician can be a fast,rewarding path. Phlebotomy technicians-frequently enough called phlebotomists-collect blood samples for testing, process specimens, and help ensure accurate lab results. Certification is a powerful credential that signals to employers you’ve earned proven skills and knowledge.
In this guide, you’ll find a clear path to certification, practical tips for choosing the right school, and a curated look at top phlebotomy technician programs. Whether you want an affordable community college certificate or a more hands-on private program with extensive practicum, this article will help you navigate your options and start your healthcare career with confidence.
What is a Phlebotomy Technician?
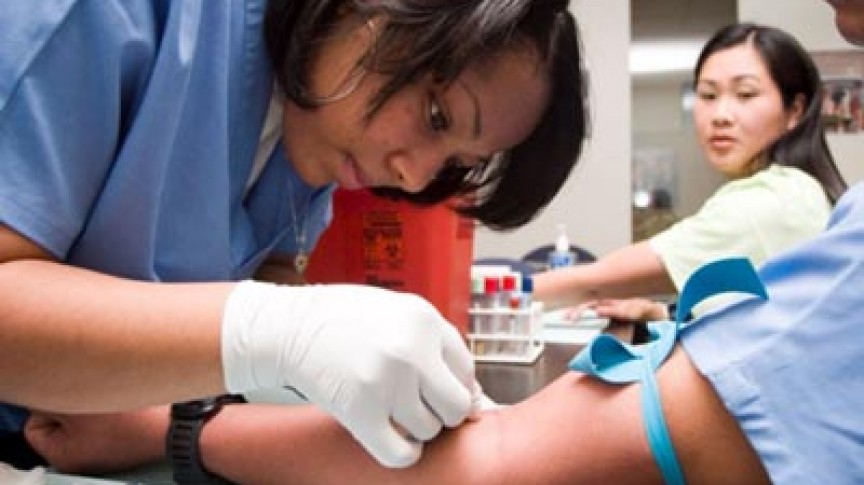
A phlebotomy technician specializes in obtaining blood samples from patients or donors for tests, transfusions, or research. Core duties typically include:
- Explaining procedures to patients and addressing fears with empathy
- Preparing and labeling specimens accurately
- Using proper venipuncture and capillary techniques
- Maintaining cleanliness, safety, and infection control standards
- Documenting procedures and specimen conditions
Because this role touches patient care and laboratory work, many employers prefer candidates who hold a formal certificate or certification from a recognized certifying body.
Why Certification matters
Certification demonstrates competency in essential skills,supports consistent patient safety practices,and can expand employment opportunities. Benefits include:
- Higher employability and potential for better starting pay
- Access to a broader range of clinical settings (hospitals, clinics, blood banks)
- Clear credentialing that meets many employer expectations
- continued professional growth through recertification and CE requirements
Note: Certification requirements vary by state and employer. Some states require licensure or additional credentials, and some employers may accept multiple certifying bodies. Always verify local licensing or employment requirements for your area.
How to Become a Certified Phlebotomy Technician: Step-by-Step
- Research local requirements: Check whether your state or city requires licensure or has specific credentialing rules for phlebotomists. This helps you choose the right program from the start.
- Choose a reputable phlebotomy program: Look for programs accredited by recognized bodies, with hands-on clinical practicum, and a clear pathway to certification.
- Complete coursework and practicum: Most programs combine classroom learning (anatomy, physiology, safety, specimen handling) with supervised blood collection in a clinical setting.
- Earn your certificate and meet eligibility for certification exams: Upon program completion, you’ll typically be eligible to sit for one or more national certification exams offered by major certifying organizations.
- Pass a national certification exam: Choose a certifying body that aligns with your goals (see options below). Passing the exam validates your skills and trains you for professional practice.
- Maintain certification: Expect to complete continuing education units (CEUs) at regular intervals to renew your credential and stay current with best practices.
Popular certifying bodies include the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP) with its phlebotomy Technician (PBT) certification, the National Healthcareer Association (NHA) Certified Phlebotomy Technician (CPT), and the American Medical technologists (AMT) registered Phlebotomy Technician (RBT). Some programs also prepare you for AMT’s RBT or AMT’s CPT designation, depending on track and state alignment.
Top Phlebotomy technician Schools: how to Choose and What to Expect
When evaluating schools, look for programs that offer strong clinical experiences, experienced instructors, flexible scheduling, and transparent costs. Below are common program formats and what they typically offer:
Program Formats to consider
- Community college certificate programs: Often the most affordable and accessible option with robust clinical partnerships.
- Private vocational or career schools: Usually intensive, focused on job-ready skills, and with structured practicum components.
- Online programs with local practicum: Great for flexible schedules if you can secure a local clinical site for hands-on training.
- Hospital or clinical partner programs: Direct-pathway routes via affiliated hospitals, sometimes with guaranteed practicum placements.
What to Look For in a School
- Accreditation and recognition by certifying bodies
- Clinical practicum hours and placement support
- Curriculum alignment with certification exams (PBT, CPT, RBT)
- Flexible scheduling, including evenings or weekends if you’re working
- Transparent tuition, fees, and available financing options
Table: Fast comparison of Program Formats
| format | Pros | Cons | Typical Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community College Certificate | Lower cost; strong clinical partnerships; local access | Large classes; may have waitlists | 8-16 weeks |
| Private Vocational School | Intensive, job-focused; modern facilities | Higher tuition; shorter timelines may mean concentrated schedules | 6-12 weeks |
| Online Program with Local Practicum | Flexibility for working students; self-paced options | Needs strong self-discipline; requires a nearby site for practicum | 6-18 weeks |
Cost, Time Commitments, and Financing Your Education
Understanding cost and time helps you plan effectively. While prices vary by location and program type, here are typical ranges and considerations:
- Program tuition frequently enough ranges from about $600 to $6,000, depending on whether you choose a community college certificate, private school, or hybrid/online option.
- Additional fees may include supplies, books, background checks, and lab fees.
- Most programs require a time commitment of 8-18 weeks, with practicum hours ranging from 40-120 hours depending on the curriculum.
- Financing options can include federal financial aid (for eligible students), scholarships, payment plans, and employer reimbursement programs.
Tip: if cost is a concern, start with a community college program first. They frequently enough provide a solid foundation at a lower cost, and you can pursue specialty certifications later as needed.
Benefits and Practical Tips for Prospective Students
- Choose an accredited program that aligns with the certification you plan to pursue.
- Seek programs offering robust clinical practicum placements-hands-on experience is essential.
- Ask about the pass rates for the certification exams the school prepares you for.
- Build a study plan early. Use official exam prep guides,flashcards,and practice tests.
- Connect with alumni or current students for real-world insights into the program and job market.
Case Studies and first-Hand Experiences
Real-world stories can illuminate what to expect:
- Case Study A: A student balancing a full-time job completed a 12-week online-based phlebotomy certificate with evening practicum hours. After certification, they secured an entry-level position at a local clinic and reported strong patient interaction skills as a key strength learned during practicum.
- Case Study B: A student attended a community college program with a 100-hour practicum. They consistently achieved top marks in specimen handling and where offered a hospital internship during the final weeks. Certification followed, leading to a role in a hospital outpatient lab.
Practical Tips to Prepare for Certification
- Study the core topics: anatomy and physiology relevant to venipuncture, infection control, patient communication, specimen handling, and safety procedures.
- Practice phlebotomy technique under supervision in the lab to build technical confidence before clinical work.
- Familiarize yourself with the equipment used in your program and the steps of the blood collection process.
- develop strong documentation habits early-accurate labeling, time stamps, and chain-of-custody practices matter for exams and real-world work.
- Plan ahead for the certification exam: register early, review official exam blueprints, and take multiple practice tests.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does a phlebotomy technician do day-to-day?
Most days involve collecting blood samples, labeling specimens, maintaining sterile technique, helping patients feel at ease, and coordinating with lab personnel to ensure specimens are transported correctly.
Do I need certification to work as a phlebotomy technician?
Certification is highly preferred by employers and frequently enough required for many roles. Some states or hospitals may have additional requirements, so check local regulations.
Which certification is best?
Common options include ASCP PBT, NHA CPT, and AMT RBT.choose a certifying body that aligns with your region, employer preferences, and your training program.
How long does it take to become certified?
Most programs take about 8-18 weeks to complete. After graduation, preparing for and passing the certification exam may take a few weeks depending on your study pace.
How often do I need to recertify?
Most certifying bodies require renewal every 2-4 years, with continuing education or re-exam options to maintain the credential.
Conclusion: Start Your Phlebotomy Journey Today
Becoming a certified phlebotomy technician is a practical and rewarding way to enter the healthcare field quickly. By choosing a reputable program, completing the required clinical practicum, and passing a recognized certification exam, you’ll position yourself for meaningful work in clinics, hospitals, and laboratories. Use this guide as your roadmap to research programs,compare costs,and prepare for success in both certification and your new career.
Ready to take the next step? Start by identifying local programs that fit your schedule and budget, verify their alignment with certification bodies, and reach out to admissions counselors to discuss financing and practicum opportunities. Your path to becoming a certified phlebotomy technician starts with a single,informed decision.
For more personalized guidance, consult with career services at your chosen school or contact local laboratories to understand what employers in your area value most in a phlebotomy technician.
Meta note: Remember that requirements can change by state and employer. Always verify current rules before enrolling.